 If you've ever eaten a Camp Joy cherry tomato you'll know why I was excited to be given a tour of the new seedlings in the greenhouse by Jim Nelson, the creator of this beautiful, organic family farm. Since 1971 this non-profit farm has been providing educational, creative programs for kids and adults. It is an example of and encourages others who wish to begin their own sustainable farm.
If you've ever eaten a Camp Joy cherry tomato you'll know why I was excited to be given a tour of the new seedlings in the greenhouse by Jim Nelson, the creator of this beautiful, organic family farm. Since 1971 this non-profit farm has been providing educational, creative programs for kids and adults. It is an example of and encourages others who wish to begin their own sustainable farm.
It was a warm, spring day when I visited and Jim was gently watering the herb, vegetable and flower seedlings by hand using water from a large can that had warmed to room temperature and given off any chlorine that was present. Camp Joy has a spring plant sale coming up April 27th and 28th and another on Mother's Day weekend and Jim was pleased with the progress of the seedlings. They grow proven varieties that do well in our area. Group paintings done by charter school children decorated the wall of the greenhouse.
Outside we were accompanied by Jim's two dogs, Ruby and Rownya, as we admired the garlic crop that will  be braided after harvest and offered for sale in the fall along with dried flower wreaths and onion braids.
be braided after harvest and offered for sale in the fall along with dried flower wreaths and onion braids.
The farm offers a Camp Joy Cooperative weekly for 3-5 yr olds encouraging them to explore their surroundings through all their senses. Garden tours for school age children or a group of any age are also offered. Everyone at the farm is happy to share what they've learned about growing and preparing food, saving seed, bees and other insects, goats and garden crafts. And there is always something to be picked, harvested, weeded or just enjoyed while having lunch in the gazebo.
Walking along a path bordered by phlox, aster, oregano, iris and nigella we admired a blooming Buff Beauty rose covering an arbor. Jim planted this as well as his favorite Madame Alfred Carrier 42 years ago when he first came to the property. His friend at UCSC, Alan Chadwick introduced him to it. The soft fragrance blended with the blooming lilacs and wisteria.
To maintain fertile soil, a cover crop of fava beans was just starting to bloom in a several areas. Ladybugs were plentiful on the flowers. The beans will be cut down, Jim explained, in about a month. Members of the farm will eat some of the beans while young and sweet and let some mature so they can save the seed. The goats also enjoy fava beans at the flowering stage. There is a fund-raising art program, called Kids for Kids, offered in May, the proceeds going to help improve the goat barn and yard.
 Next we visited the Kid's Garden. Art, cooking and gardening projects are ongoing in this area. Wholesome, healthy food and beautiful flowers are all part of the farm. The plot of godetia was setting bud and will be offered as cut flowers during the upcoming sales.
Next we visited the Kid's Garden. Art, cooking and gardening projects are ongoing in this area. Wholesome, healthy food and beautiful flowers are all part of the farm. The plot of godetia was setting bud and will be offered as cut flowers during the upcoming sales.
Everything is grown with care at Camp Joy. Jim explained that compost is regularly added back to the soil and used to start seedlings in a special blend of "real soil" allowing them to transplant and continue to do well in the garden. He sometimes used kelp and fish emulsion as fertilizer but mostly it's the compost that makes the seedlings so strong.
Camp Joy offers lots of classes for kids and adults alike. Family members and interns are passionate about the farm and enjoy sharing. On this beautiful day, we were greeted with a smile by the person spreading compost. It was clear that there is a respect for the cycles of the earth and the changing seasons at the farm.
Take advantage of the Spring Plant Sale at Camp Joy. Bring the family and walk through the garden. Visit their website for more information about their events and classes. http://www.campjoygardens.org

 Linda Butler starts all her vegetables from seed, and grows year-round. Some are started directly in the beds while others are started in flats and transplanted later. Cole crops, such as broccoli, cauliflower and cabbage, would get eaten by bugs and birds would eat them as fast as they germinated so these are started in flats.
Linda Butler starts all her vegetables from seed, and grows year-round. Some are started directly in the beds while others are started in flats and transplanted later. Cole crops, such as broccoli, cauliflower and cabbage, would get eaten by bugs and birds would eat them as fast as they germinated so these are started in flats.  Steven, started the farm in 2007. Their 90 acres is zoned mixed agriculture but since some of it encompasses rare Ben Lomond sandhills habitat, they farm just a couple of acres. They have even installed a wide deer corridor separating the growing areas to allow the deer access to their feeding and watering places.Tall fences protect the beds from other critters but they encourage the birds and bees by planting flowers that seed, attract beneficial insects and produce pollen.
Steven, started the farm in 2007. Their 90 acres is zoned mixed agriculture but since some of it encompasses rare Ben Lomond sandhills habitat, they farm just a couple of acres. They have even installed a wide deer corridor separating the growing areas to allow the deer access to their feeding and watering places.Tall fences protect the beds from other critters but they encourage the birds and bees by planting flowers that seed, attract beneficial insects and produce pollen.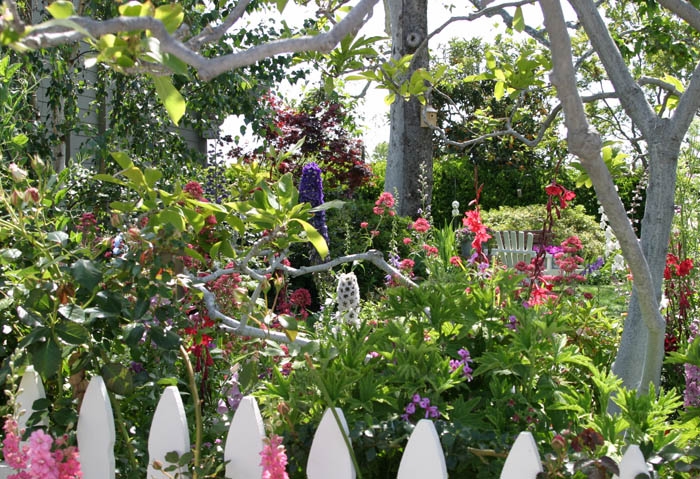  start with well composted manure because fresh manure may contain E. coli bacteria. If you buy composted manure or sufficiently compost your own, the E. coli should be long gone. Manure from animals raised organically usually do not have e. coli or salmonella in their gut. The Maine Organic Farmers and Gardeners Association recommends that manure tea be applied 60 days before harvesting vegetables and 120 days before harvesting root crops just to be sure. Cow manure is the most common type used but composted horse, rabbit, chicken or sheep manure can also be used.
start with well composted manure because fresh manure may contain E. coli bacteria. If you buy composted manure or sufficiently compost your own, the E. coli should be long gone. Manure from animals raised organically usually do not have e. coli or salmonella in their gut. The Maine Organic Farmers and Gardeners Association recommends that manure tea be applied 60 days before harvesting vegetables and 120 days before harvesting root crops just to be sure. Cow manure is the most common type used but composted horse, rabbit, chicken or sheep manure can also be used. the plants in the garden come to life. I’ve been invited to tour a garden in Scotts Valley in April when many of the early flowering plants will be in bloom. I’ve been to this garden before and there’s always an interesting tree, shrub or flower to enjoy.
the plants in the garden come to life. I’ve been invited to tour a garden in Scotts Valley in April when many of the early flowering plants will be in bloom. I’ve been to this garden before and there’s always an interesting tree, shrub or flower to enjoy.  refers to the position in the sky of the constellation Leo, the lion, at the beginning of the month and Aries, the ram or lamb, at the end. As I write this week’s column, the saying rings true so far this month. Beautiful weather and more daylight hours to enjoy it. What’s not to like?
refers to the position in the sky of the constellation Leo, the lion, at the beginning of the month and Aries, the ram or lamb, at the end. As I write this week’s column, the saying rings true so far this month. Beautiful weather and more daylight hours to enjoy it. What’s not to like?